Application scope
With constant pressure to increase efficiencies and reduce costs, many organisations are turning to robotic process automation (RPA) as a solutition.
Robotic Process Automation is well suited for processes that are clearly defined and well documented, repeatable without many changes and also if they are rules-based. Based on criteria mentioned, it helps organizations across numerous industries automate the completion of a wide variety of tasks.
Finance & Accounting
Historically, finance team responsibilities include a number of highly manual and time-intensive processes such as account reconciliations and manual journal entries. One of the challenges for their workforce is to perform these tasks without any error as faulty data and discrepancies usually lead to additional expenses and additional costs that significantly disrupt the workflow.
Especially accounting contains a lot of processes that are high-transaction, repeatable, well structured, rules-based processes that lend themselves to robotic process automation. RPA robots have the same work instructions as humans and have the same access rights to the required programs in order to carry out the required process steps. But they work much faster, more efficient and less prone to errors than human employees.

Some of the areas RPA is used in the financial services
- Customer onboarding
- Master data maintenance
- Portal queries
- Data Management
- Reminder and invoice processing
- Supplier onboarding
- Price comparisons
- Supporting financial close
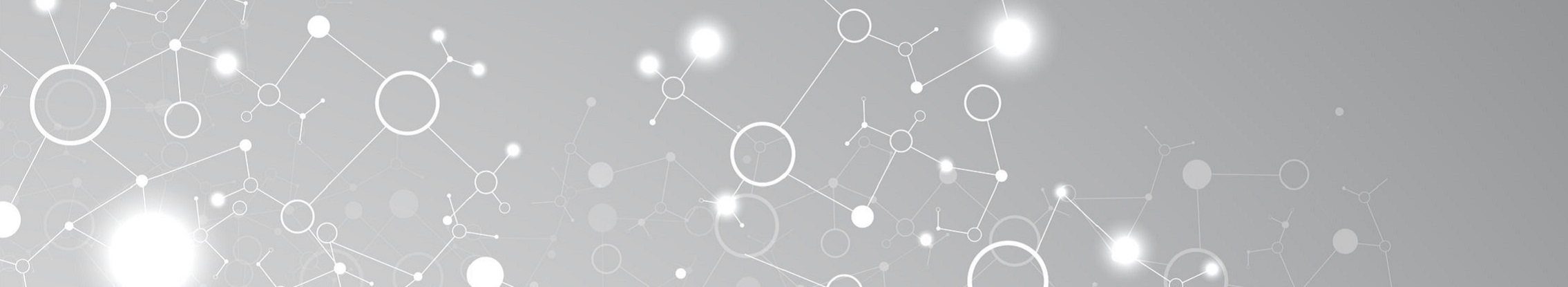
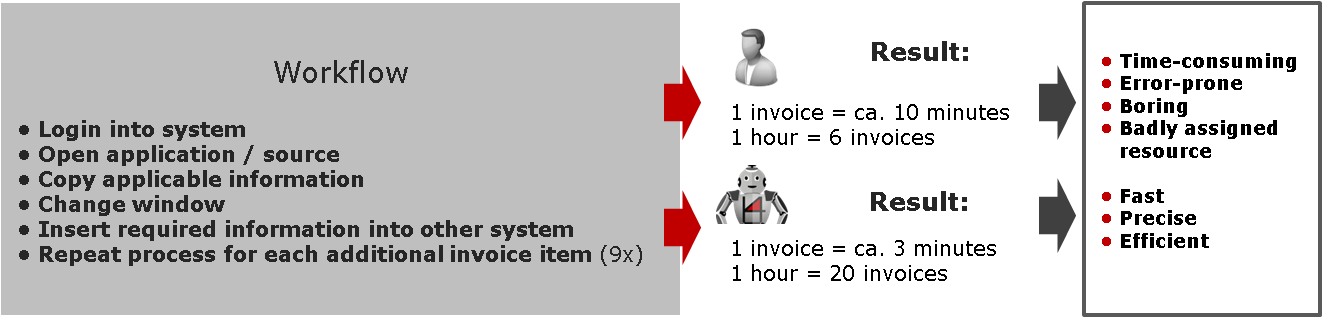
Example: Invoice processing
Creating an invoice with 10 different invoice items, equiring basic data from various sources and systems faster and more accurate with RPA.
Human Resources
Despite an increasing degree of digitization, many HR departments are still heavily dependent on manual-driven processes , many of which are voluminous, repetitive, time-consuming.

Utilizing RPA saves a considerable amount of time that can be used for various other nuanced strategic issues, including employee training and personal interviewing.
Wherever processes are repetitive, rule-based, error-prone, seasonal and time-critical, b4 bots can take over the tasks. This reduces the processing costs and increases the quality and efficiency of the individual processes.
RPA in Human Resources
- Employee Acquisition and Data Management
- Document management
- Onboarding
- Offboarding
- Time and attendance recording
- Travel Expenses
- Payroll
- Reports and analyzes
Revolutionize Your Recruitment Process by adding RPA and AI to
your Human Capital Management (HCM)
See White paper
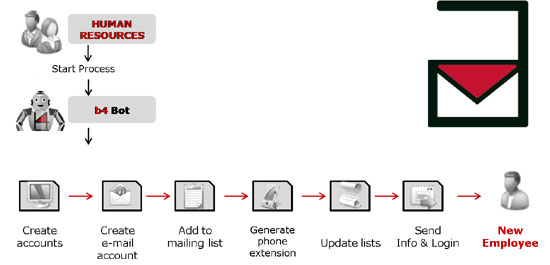
Onboarding Process
Employee onboarding is one of the first activities to be automated in Human Resources.
Taking onboarding of new hires as an example - for every new hire, IT hardware, user account, e-mail-address, accesses etc. need to be requested.
Based on predifined graphical rules, these activities can be executed by the b4 Bot.
Customer Service
 Companies across industries are adopting intelligent automation as part of their digital transformation strategy to become more efficient, boost customer service and increase revenues.
Companies across industries are adopting intelligent automation as part of their digital transformation strategy to become more efficient, boost customer service and increase revenues.
Direct communication with customers is an extremely important, but often a delicate matter. Alone due to the mass of inquiries it is hardly possible for many companies to process everything manually in an acceptable time.
The consequences are dissatisfaction and poor ratings due to delayed or inappropriate responses. RPA-Bots can help process, filter and often even answer customer inquiries with standardized outputs. At the same time, the software can evaluate the content of complaints and thus contribute to the improvement of products and service.
Customer-oriented processes
- Chatbots for pre-selection of concerns
- Terminanlage
- Scheduling
- Complaint management
- Cancellation management
- Ticket processing
- Data management and migration
Procurement
Procurement is, by nature, in the business of relationships. Whether it’s managing suppliers or stakeholders, the success of any procurement organisation relies heavily on building relationships between people. At the same time, procurement function has always involved processes which are concerned with data collection, manual data entries,reporting, transactional activities, urgencies, etc.

Many procurement processes include highly repetitive tasks which not only consume a larger time of workforce but are also prone to human error. RPA reduces labor-intensive activities, resulting in cost savings of 30-60 percent. However, the advantages of process automation by software robots go far beyond pure cost optimization. RPA bots work much faster and far more precise than humans. This drastically reduces throughput times of the delegated processes, virtually eliminates error rates and increases process quality.
Uses of RPA in Procurement Process
- Purchase request to Purchase Order
- Demand and Supply Planning
- Inventory Management
- Work order Management
- Invoice Processing
- Reporting
Logistics
 The availability of all important documents and data regardless of time and place is of crucial importance in the transport and logistics industry. However, many companies in this industry still rely on manual execution of their business-critical processes in more than half of their processes.
The availability of all important documents and data regardless of time and place is of crucial importance in the transport and logistics industry. However, many companies in this industry still rely on manual execution of their business-critical processes in more than half of their processes.
Business processes in the transport and logistics industry are heavily dependent on back-office activities and consist to a large extent of routine routine activities. Everyday tasks, which take place on a large scale, require a great deal of time and resources and are also prone to error.
Using robotic process automation, unloved, low-volume mass tasks are performed by software robots, with over 99% reliability. Valuable resources, which were previously bound by such tasks, can be used in a variety of different, demanding and therefore more motivating ways.
- Document capture / processing
- Complaints and claims handling
- Billing and accounting
- Goods receipts and exits
- Order planning and monitoring
- Inventories
Healthcare
Healthcare providers across the globe carry out multiple procedures and tasks which are managed or monitored manually. With this approach, executing and tracking these procedures along with core tasks can be tedious, time-consuming, and error-prone. Additionally, healthcare institutions must ensure compliance for various rules and regulations.
Autonomics and multi-agent systems in healthcare allow for the growth and development of definable, repeatable, and rule-based processes. Robotic process automation serves as a competitive advantage, not replacing humans in the care-giving/healthcare delivery process, but enabling them to focus on more personalized treatments, and higher-level processes.
Rely on a digital RPA workforce
With RPA, almost any repetitive process can be automated and subsequently scaled.
There are a number of processes in the healthcare industry for using RPA bots:
- Patient record transfers
- Claims processing
- Billing
- Scheduling
- Copy history and treatment data into multiple systems
- Enter and synchronize patient data
- Nutrition plan management
- Reporting
Software-Testing
As most people in the software industry know, there are distinct differences between manual testing and automated testing. Manual testing requires physical time and effort to ensure the software code does everything it’s supposed to do. In addition, manual testers have to make a record of their findings.
This is not only time consuming, but makes it difficult to thoroughly test an application prior to release. If defects slip undetected into the production environment, the result can be customer dissatisfaction and increased maintenance costs.
Test Automation with b4 allows your team to execute more tests in less time, increasing coverage and freeing human testers to do more high-level, exploratory testing. b4 Test Automation is especially beneficial for test cases that are executed repeatedly, such as those for cross-browser and cross-device compatibility, and those that are part of a full or partial regression suite.


